
In order to use a date in Python, you first need to import a module named datetime. The datetime module has various class types, but the most common use of class types is class datetime which is a combination of a date and a time. Do not confuse datetime() class (constructor) with datetime module. They just have same name.
Its attributes are year, month, day, hour, minute, second, microsecond in sequence order.
import datetime
currentTime = datetime.datetime.now()
print(currentTime.year)
print(currentTime.month)
print(currentTime.day)
print(currentTime.hour)
print(currentTime.minute)
print(currentTime.second)
print(currentTime.strftime("%A")) # day of weekThe last example of strftime is a method for formatting date objects into human readable strings. strftime() method takes one parameter, something similar to regular expression. You can check all the legal format codes below if you’re not sure what parameter you choose.
datetime.datetime.strftime(parameter)
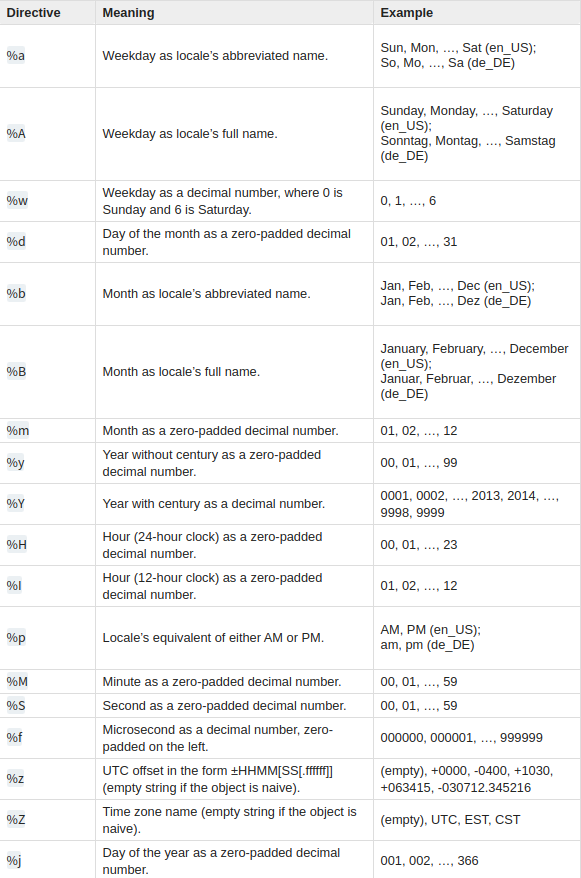
references: https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/datetime.html